Imagine a world where machines understand your needs, learn from their surroundings, and act with purpose. Welcome to the world of AI agents—intelligent systems designed to perceive, think, learn, and act autonomously. You may not know it, but you probably interact with AI agents every day, whether you’re asking Alexa to play your favorite song, chatting with a customer support bot, or receiving personalized recommendations on Netflix.
AI agents are becoming a foundational part of modern technology, transforming industries, daily life, and the future of work. But what exactly are AI agents? How do they function, and why are they so impactful? In this blog, we’ll break down everything you need to know—from their inner workings and real-world examples to their benefits and future potential.
So, buckle up. This isn’t just another tech buzzword. AI agents are shaping the world as we know it—and it’s time you knew how.
Defining AI Agents
Let’s start with the basics—what are AI agents?
In the simplest terms, an AI agent is a software system (or sometimes a hardware system) that perceives its environment through sensors and acts upon it using actuators. Think of it as a self-sufficient digital brain with the ability to sense, think, and respond.
But it doesn’t stop there.
AI agents aren’t just reactive; many are designed to learn from past experiences, adapt to new inputs, and even make decisions without human intervention. This is what separates them from traditional software applications that follow predefined instructions.
The concept of AI agents stems from artificial intelligence research, particularly in the field of autonomous systems. Inspired by how humans and animals interact with the world, AI agents are meant to operate independently, often in unpredictable or dynamic environments.
They can be:
- Software-based, like chatbots or recommendation engines.
- Hardware-based, like robots or autonomous vehicles.
In essence, an AI agent is like a virtual or physical robot that thinks and acts to achieve goals, often learning along the way.
Core Components of AI Agents


So, what makes an AI agent tick? Let’s break down the key components that drive these intelligent systems.
1. Perception
AI agents start by observing the environment. They use sensors (virtual or physical) to gather data. For example:
- A virtual assistant listens to voice commands.
- A robot uses cameras to detect objects.
2. Reasoning
Once data is collected, the agent needs to process it. This is where reasoning comes into play.
- Should the chatbot respond with a greeting or a solution?
- Should the self-driving car turn left or stop?
3. Learning
The most powerful agents are not hard-coded. They learn from past actions and outcomes, improving over time using machine learning algorithms.
4. Acting
After processing, the agent makes a decision and takes action. This could mean sending a message, moving an object, or launching a task. Together, these components enable AI agents to function autonomously, constantly adapting and responding to the world around them.
Types of AI Agents
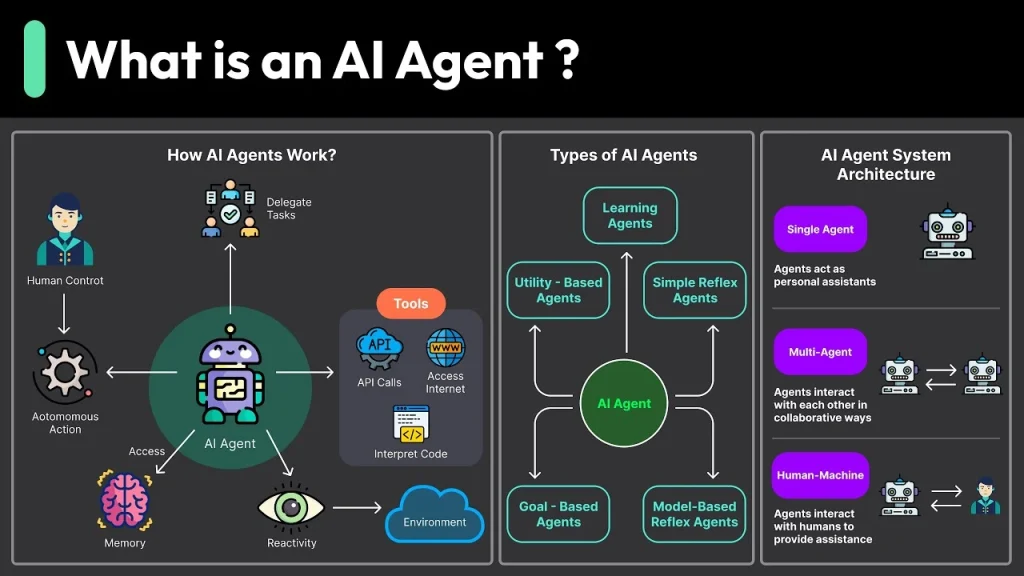

Not all AI agents are created equal. Depending on their complexity and design, they can be categorized into different types.
Simple Reflex Agents
- Work on “if-then” rules
- No memory of past actions
- Example: Thermostats
Model-Based Agents
- Maintain an internal state of the world
- Use models to interpret input
- Example: Advanced bots in games
Goal-Based Agents
- Operate with specific objectives
- Make decisions based on goal achievement
- Example: Navigation apps finding optimal routes
Utility-Based Agents
- Evaluate multiple possible outcomes
- Choose the one with the highest utility (value)
- Example: Financial trading bots
Learning Agents
- Adapt over time using feedback
- Use machine learning to improve
- Example: Email spam filters
Understanding the types helps you grasp the versatility and sophistication AI agents can achieve based on their use case.
How AI Agents Work
At their core, AI agents operate through a continuous loop of:
- Sensing
- Processing
- Decision-making
- Action-taking
This process is often visualized using the Perception-Decision-Action loop. Think of a robot vacuum:
- It senses a wall (perception).
- Processes that it can’t go forward (reasoning).
- Decides to turn right (decision).
- Moves in the new direction (action).
The more advanced an agent is, the more sophisticated its decision-making becomes. Many agents now use machine learning models, especially reinforcement learning, where they get rewards or penalties for actions, shaping their future behavior.
The environment also plays a critical role. Agents can operate in:
- Fully observable environments (all information is known)
- Partially observable environments (some information is hidden)
The more uncertain or dynamic the environment, the smarter the agent must be to perform well.
AI Agents vs Traditional Software


Let’s clear up a common misconception: AI agents aren’t just fancy software programs. While traditional software follows fixed rules and pre-written logic, AI agents are designed to adapt, learn, and make decisions independently.
Key Differences:
| Feature | Traditional Software | AI Agents |
| Adaptability | Fixed responses, rigid logic | Learns from environment and adjusts |
| Autonomy | Requires frequent human input | Operates independently |
| Learning | No learning capabilities | Can use ML to improve over time |
| Environment Response | Limited to pre-programmed situations | Reacts dynamically to real-time changes |
Imagine a spam filter in your email. A traditional one blocks emails based on static rules. But an AI agent-based filter learns what you personally consider spam, adapting its behavior over time.
That’s the magic: AI agents don’t just follow commands—they understand intent and evolve to serve better.
Real-World AI Agents Examples
To make things more tangible, let’s look at some real-world AI agents examples that you’ve probably encountered or benefited from without even realizing it.
1. Virtual Assistants (e.g., Siri, Alexa, Google Assistant)
- Understand your voice commands
- Learn your preferences
- Perform actions like setting reminders or playing music
2. Self-Driving Cars
- Sense the environment using cameras and LiDAR
- Make real-time decisions (like braking or changing lanes)
- Continuously learn from road conditions and driving patterns
3. Recommendation Engines
- Used by Netflix, YouTube, Amazon
- Learn what you like based on your behavior
- Suggest movies, videos, or products tailored just for you
4. Customer Support Chatbots
- Answer common queries
- Escalate complex issues to humans
- Improve responses through natural language processing
5. Smart Home Devices
- Thermostats adjust based on your schedule
- Lights turn off when no one’s home
- Security cameras analyze movement patterns
These AI agents improve convenience, efficiency, and personalization. And this is just the beginning. As more industries adopt AI agents, their impact will multiply.
Benefits of AI Agents
So, why all the hype? What are the real, tangible benefits of AI agents?
Let’s break it down.
1. Increased Efficiency
AI agents can perform tasks faster and more accurately than humans. They automate repetitive and time-consuming activities, freeing up valuable human time for more creative or strategic work.
2. Scalability
One AI agent can serve millions of users simultaneously without fatigue or downtime. Think about how a single chatbot can assist thousands of customers 24/7.
3. Improved User Experience
Personalization is the name of the game. AI agents learn from individual behavior, offering tailored recommendations, responses, or services.
4. Cost Savings
Businesses can significantly cut costs by deploying AI agents for customer support, data analysis, and operational management.
5. Real-Time Decision Making
AI agents analyze massive datasets in real time, enabling faster and smarter decisions—essential for things like fraud detection or stock trading.
6. Continuous Learning
Thanks to machine learning, AI agents don’t just execute; they evolve. The more they operate, the better they get.
Simply put, AI agents aren’t just useful—they’re transformative.
AI Agents in Business Applications
In the business world, AI agents are game changers. They’re helping companies innovate, save money, and stay competitive.
1. Customer Support
AI-powered chatbots and virtual agents can:
- Handle FAQs
- Route queries to appropriate teams
- Offer instant, accurate responses
2. Marketing and Sales
- AI agents analyze customer behavior
- Create personalized ad campaigns
- Score leads and predict conversion rates
3. Financial Forecasting
- Use historical data and market trends
- Predict revenue, expenses, or investment risks
- Help CFOs and analysts make informed decisions
4. Inventory and Supply Chain Management
- Monitor stock levels in real time
- Predict product demand
- Optimize delivery routes using real-time data
These applications lead to streamlined operations, better decision-making, and enhanced customer engagement.
AI Agents in Everyday Life
Beyond business, AI agents are becoming integral to our everyday experiences.
1. Smart Homes
- AI agents in devices like thermostats, lights, or vacuum cleaners
- Automate home routines based on behavior
- Make homes more energy-efficient and comfortable
2. Healthcare
- Virtual health assistants schedule appointments
- AI triage bots ask symptoms and guide users
- Wearables powered by AI agents track health stats
3. Education
- AI tutors offer personalized learning
- Language learning apps adapt to your pace
- Automated grading saves time for teachers
4. Entertainment
- Streaming platforms curate content
- Music apps create personalized playlists
- Video games use intelligent NPCs (non-player characters)
As AI agents become more embedded in everyday tools, they will quietly reshape how we live, learn, and connect.
Challenges and Limitations


AI agents are powerful—but they’re not perfect. Several challenges and limitations still exist.
1. Ethical Concerns
- Should AI agents make life-impacting decisions?
- What if a self-driving car has to choose between two harmful outcomes?
2. Bias and Fairness
AI agents can inherit human biases from training data. This can lead to:
- Discrimination in hiring tools
- Skewed financial assessments
- Misjudgments in legal or healthcare decisions
3. Data Privacy
To learn and operate, AI agents need data—your data. Without proper safeguards, this raises serious privacy concerns.
4. Reliability
Can AI agents be trusted to act correctly in all situations? While they’re improving, edge cases and rare situations can still confuse them.
5. Transparency
Many AI agents operate as black boxes—we don’t always know how they arrive at their decisions. That’s a big deal when dealing with critical tasks like medical diagnoses.
While AI agents offer enormous value, they must be implemented ethically, responsibly, and with clear human oversight.
AI Agents and Machine Learning
You can’t talk about AI agents without diving into machine learning (ML). Why? Because ML is the engine that makes AI agents smarter over time.
AI agents aren’t just rule-based programs anymore. Thanks to ML, they can recognize patterns, learn from data, and improve their performance without being explicitly programmed for every scenario.
How ML Powers AI Agents:
- Supervised Learning
- AI agents learn from labeled data.
- Example: An email filter learns what is spam and what isn’t by analyzing thousands of labeled emails.
- Unsupervised Learning
- AI agents identify patterns in unlabeled data.
- Example: Grouping customer behavior into clusters for targeted marketing.
- Reinforcement Learning
- AI agents learn through trial and error by receiving rewards or penalties.
- Example: A robot learning to walk or a game AI mastering strategy through feedback.
Machine learning makes AI agents adaptive, personalized, and smarter with every interaction. It’s why your Netflix recommendations get better the more you watch or why a chatbot starts understanding your tone over time.
In a nutshell, ML is the brain, and the AI agent is the body—working together to act intelligently in the world.
Security Aspects of AI Agents
With all their intelligence, AI agents also raise some serious security concerns. And as they handle more critical tasks—from financial transactions to medical advice—keeping them secure is non-negotiable.
1. Data Privacy
AI agents collect and process huge amounts of personal data. Without proper encryption and data protection, this can lead to:
- Data breaches
- Identity theft
- Unwanted surveillance
2. Adversarial Attacks
Some AI agents can be tricked by manipulated inputs—called adversarial attacks.
- Example: Slightly altering a stop sign image could confuse a self-driving car into thinking it’s a speed limit sign.
3. Unauthorized Access
If an AI agent isn’t properly secured, hackers could hijack it to:
- Control smart devices
- Access sensitive information
- Disrupt operations
4. Compliance
With regulations like GDPR, companies must ensure that AI agents:
- Are transparent about data usage
- Allow users to control or delete their data
- Don’t make fully automated decisions without oversight
In short, AI agents must be built with security as a foundation, not an afterthought. A smart agent isn’t very useful if it can be easily compromised.
Future of AI Agents


So, where is all this heading? The future of AI agents looks bright—and wild.
1. Hyper-Personalization
Imagine AI agents that know you better than your best friend. From healthcare to shopping, everything will be custom-tailored based on your behavior, mood, and preferences.
2. Multi-Agent Systems
Instead of one AI agent, you’ll interact with a network of agents working together, each specialized in a task:
- One manages your calendar.
- Another handles finances.
- A third plans your travel.
They’ll communicate and collaborate seamlessly.
3. Emotional Intelligence
AI agents will go beyond logic and start understanding emotions. Think of customer support bots that can sense frustration and respond with empathy—or virtual therapists that detect depression symptoms early.
4. Human-AI Collaboration
Rather than replacing humans, future AI agents will act as co-pilots, helping us make better decisions:
- Doctors using AI agents to assist with diagnostics
- Writers using AI agents for content research and ideation
- Engineers using them for real-time design feedback
5. General AI Agents
We may eventually see agents that learn across multiple domains—from finance to language to robotics—pushing the boundaries of what AI can do.
One thing is certain: AI agents will be deeply woven into our lives, reshaping how we live, work, and interact with technology.
Conclusion
By now, you should have a clear picture of what AI agents are—and why they matter more than ever.
From self-driving cars and virtual assistants to recommendation engines and customer service bots, AI agents are the silent architects of our digital world. They perceive, think, act, and learn—making our lives easier, our businesses smarter, and our future more connected.
Whether you’re a tech enthusiast, a business owner, or just a curious mind, understanding AI agents is crucial. They’re not a far-off concept—they’re here, and they’re evolving fast.And as AI continues to grow, one thing is certain: AI agents will be at the heart of the next digital revolution.
FAQ
What are AI agents in simple terms?
AI agents are intelligent systems—either software or hardware—that observe their environment, make decisions, and take actions based on what they’ve learned.
How are AI agents used in real life?
They’re used in virtual assistants like Siri, self-driving cars, recommendation engines (like Netflix), smart home devices, and customer support bots.
Are AI agents the same as robots?
Not always. While some robots are AI agents, many AI agents are purely software-based and don’t have a physical form.
What makes AI agents better than traditional software?
AI agents can learn, adapt, and make decisions autonomously, whereas traditional software follows fixed rules without learning from experience.
What’s the future of AI agents?
Expect smarter, more personalized, emotionally aware agents that collaborate with humans and work across different domains to simplify life and business.




